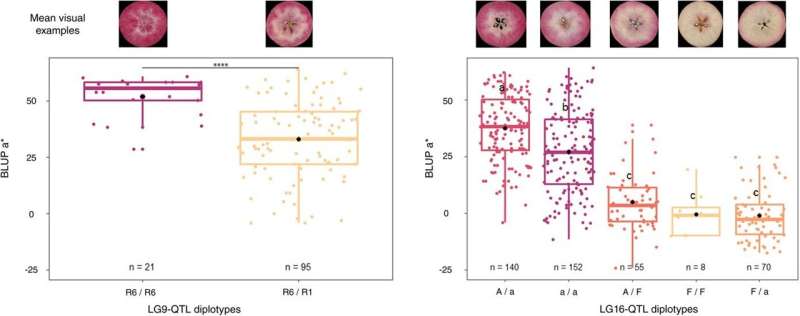
Distribution of BLUP* for RF1-5 offspring haplotypes for LG9-QTL (left) and five offspring F1 haplotypes for LG16-QTL (right). Credits: Horticultural Research (2024). DOI: 10.1093/hr/uhae171
The bright red color of apples appeals to breeders and consumers, offering visual appeal and potential health benefits due to their high anthocyanin content. However, the genetic complexity behind this trait has not been investigated, as most studies focus on anthocyanin concentrations.
To address this gap, an in-depth study of genetic factors and phenolic interactions is critical for improving red apple breeding. A new study was carried out and published by a team from the University of Angers and the Institut Agro Horticultural Researchinvestigated the genetic structure of red-flesh in apple using pedigree-based quantitative trait loci (QTL) mapping.
The team analyzed 452 genotypes from five interbreeding F1 families, highlighting genetic regions that influence flesh color and phenolic profiles, providing valuable insights for future breeding.
The study identified 24 QTLs related to vigor and red color and phenolic profile, spanning several genes, including LG1, LG2, LG8, LG9, LG11, and LG16. An important discovery is a genetic model that expresses the competition between anthocyanin and flavan-3-ol synthesis, which greatly affects the development of red tissue.
This research shows that it is possible to increase the strength of the red color by selecting good alleles from both the red and white parents, providing a method for targeted breeding. This method goes beyond traditional color estimation by incorporating a descriptive model that captures the genetic interactions that influence apple flesh color.
The discovery of these genetic regions not only improves the understanding of the red color of red meat but also provides a useful method for breeders to breed Fresh apples have great color and potential health benefits.
Dr. Jean-Marc Celton, lead author, said, “Our research reveals the genetic complexity that causes red flesh in apples. Understanding the relationship between phenolic compounds and Genetics brings us closer to creating varieties of apples that combine remarkable colors. This research opens up new opportunities for breeding high-quality apples.”
These findings hold great promise for apple breeding programs. By targeting QTLs related to anthocyanin and flavan-3-ol balance, breeders can produce red-fleshed apples that are attractive and provide health benefits. The understanding of this study can be extended to other types of fruits with similar color patterns, which can change the improvement of agricultural crops on a wide scale.
Other information:
Pierre Bouillon et al., Finding color: quantitative analysis reveals new insights into red-flesh color in apples (Malus domestica), Horticultural Research (2024). DOI: 10.1093/hr/uhae171
References: Unlocking the genetic secrets of apple-red flesh-bitter discovery (2024, September 12) Retrieved 12 September 2024 from https://phys.org/news/2024-09-genetic- secrets-red-flesh-apples.html
This document is subject to copyright. Except for any legitimate practice for study or personal research purposes, no part may be reproduced without written permission. This content is provided for informational purposes only.
#Unraveling #genetic #secrets #applered #flesha #bittersweet #discovery